Nd:YLF
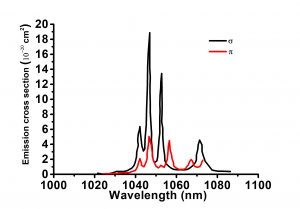
Neodymium-doped Lithium Yttrium Fluorides (Nd:LiYF4 or Nd:YLF) is a crystal which lasers at 1047 nm and 1053 nm wavelength. Its main advantages are: large fluorescence line width, low thermal lensing, low threshold for CW applications and naturally polarized oscillation, which makes Nd:YLF an excellent material for CW, mode locked operation. The term YLF laser is usually used for lasers based on neodymium-doped YLF (Nd3+:YLF) crystals, although there are other rare-earth-doped YLF crystals, e.g. with ytterbium, erbium, thulium, holmium or praseodymium doping. YLF is the acronym for yttrium lithium fluoride (YLiF4). Due to the similar size, yttrium ions can be replaced with laser-active rare earth ions without strongly affecting the lattice structure. YLF is birefringent, which eliminates thermally induced depolarization loss. Also, the gain and the emission wavelength of Nd:YLF are polarization-dependent: there is the stronger 1047-nm line for π polarization, and a weaker one at 1053 nm for σ polarization. The 1053-nm line fits well to the gain peak of Nd:glass, which makes Nd:YLF seed lasers and preamplifiers suitable for Nd:glass amplifier chains. There are additional transitions at 1321 nm (π) and 1313 nm (σ), which allow for, e.g., red light generation via frequency doubling. The negative thermo-optic coefficient dn / dT leads to a defocusing thermal lens, which may be approximately compensated by the focusing lens from bulging of the end faces, if a suitable design is chosen. Nd:YLF lasers can be diode-pumped or lamp-pumped. Compared with Nd:YAG (→ YAG lasers), Nd:YLF has a lower thermal conductivity, but nevertheless exhibits weaker thermal distortions (due to the weakly negative dn / dT), thus allows a better beam quality, has significantly anisotropic thermal expansion and a lower fracture resistance (limiting the output power), and a longer upper-state lifetime (which is favorable for, e.g., diode-pumped Q-switched lasers with high pulse energy). Another remarkable feature is the high UV transparency, which is favorable for pumping with xenon flashlamps.
Parameter
| Parallelism | <10〞 |
| Perpendicularity | <5ˊ |
| Surface Quality | better than 10/5 Scratch/Dig per MIL-O-13830A |
| Wavefront Distortion | <λ/4 per inch@632.8 nm |
| Surface Flatness | <λ/10 @632.8 nm |
| Clear Aperture | Central 90% |
| Diameter Tolerance | +0.0/-0.1 mm |
| Length Tolerance | +/-0.5mm |
| Chamfer | 0.15mm@45° |
| Structure Symmetry | Tetragonal, I41/a |
| Lattice Constants | a=5.16, c=10.85 Å |
| Specific mass | 3.99g/cm3 |
| Melting Point | 819°C |
| Thermal Conductivity /(W·m-1·K-1) | 6.3 |
| Specific Heat(J·g-1·K-1) | 0.79 |
| Thermal Expansion /(10-6·K-1 ) | 8.3(⊥c), 13.3(||c) |
| Hardness (kg/mm2@Mohs) | 4~5 |
| Young`s Modulus /(108g/cm2) | 7.65 |
| Dopant Concentration(%) | 0.5-1.5 |
| Transmission Range | 0.18 … 6.7 µm |
| Refractive Index (@1053nm) | No=1.448, ne=1.470 |
| Loss Coefficient/cm | <0.003@1064nm |
| Thermo-optic Coefficient(10-6·K-1@ ) | -2.0(E⊥c), -4.3 (E||c) |
| Scatter Loses(%/cm) | <0.2 |
| Fluorescent Lifetime(µs) | 485@1%Nd doping |
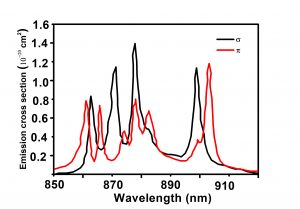
| Peak Emission Cross Section(10-19/cm2) | 1.2(E⊥c)@1053nm, 1.8(E||c)@1047nm |
| Lasing Wavelength(nm) | 1053(E⊥c, σ-pol), 1047(E||c, π-pol) |
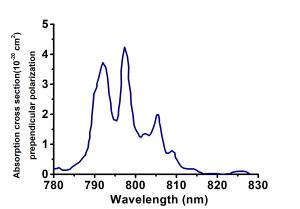
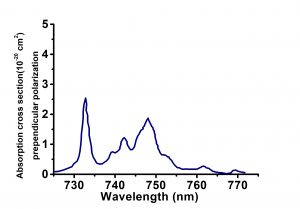
| Peak Absorption Wavelength@1.2%Nd (cm-1) | 10.8(792.0nm, E||c), 3.59(797.0nm, E⊥c) |
| λ(nm) | no | ne |
| 262 | 1.464 | 1.442 |
| 350 | 1.47 | 1.448 |
| 525 | 1.479 | 1.456 |
| 1050 | 1491 | 1.473 |
| 2065 | 1.511 | 1.485 |
- High UV transparency
- Additional transitions at 1321 nm (π) and 1313 nm (σ), which allow for, e.g., red light generation via frequency doubling
- Birefringent, which eliminates thermally induced depolarization loss
- The gain and the emission wavelength are polarization-dependent
- The 1053-nm line fits well to the gain peak of Nd:glass
- Negative thermo-optic coefficient dn/dT leads to a defocusing thermal lens
- Low thermal conductivity, but nevertheless exhibits weaker thermal distortions
- Significantly anisotropic thermal expansion and a lower fracture resistance and a longer upper-state lifetime
- YLF lasers
- Nd:YLF seed lasers and preamplifiers
- Lens
- Diode-pumped or lamp-pumped
- Diode-pumped Q-switched lasers
- Pump with xenon flashlamps
| [1] Chen M , Wang Z C , Wang B S , et al. All-solid-state ultraviolet 330 nm laser from frequency-doubling of Nd:YLF red laser in CsB3O5[J]. Journal of Luminescence, 2016. |
| [2] A Z M , A J G , B D L , et al. Thermal stress effects of the diode-end-pumped Nd:YLF slab[J]. Optics Communications, 2008, 281( 13):3522-3526. |
| [3] Oram O , Gross R L , Severin T D , et al. Picosecond neodymium:yttrium lithium fluoride (Nd:YLF) laser peripheral iridotomy.[J]. American Journal of Ophthalmology, 1995, 119(4):408-14. |
| [4] Yasumoto M , Tomimasu T , Nishihara S , et al. Optical damage of multi-layer mirrors for UV-FEL resonator induced with intense pico-second pulse FELs and Nd:YLF lasers[J]. Optical Materials, 2000, 15(1):59-63. |
| [5] Wang, Maorong, Zhong,等. High-order Stokes generation in a KTP Raman laser pumped by a passively Q-switched ND:YLF laser. |
| [6] Ma, Jian, Xiuhua, et al. High energy 523 nm ND:YLF pulsed slab laser with novel pump beam waveguide design[J]. Optics Communications A Journal Devoted to the Rapid Publication of Short Contributions in the Field of Optics & Interaction of Light with Matter, 2015. |
| [7] Ma Q , Mo H , Zhao J . High-energy high-efficiency Nd:YLF laser end-pump by 808 nm diode[J]. Optics Communications, 2018, 413:220-223. |
| [8] Hardman P J , Clarkson W A , Hanna D C . High-power diode-bar-pumped intracavity-frequency-doubled Nd:YAG and Nd:YLF ring lasers[J]. Optics Communications, 1998, 156(1-3):49-52. |
| [9] Shao J Z , Wang Q , Tian Z , et al. Performance of Nd:YLF laser by using crystal electrooptic Q-switch[J]. Optics & Laser Technology, 2005, 37(8):608-611. |
| [10] Men S , Liu Z , Cong Z , et al. Electro-optically Q-switched dual-wavelength Nd:YLF laser emitting at 1047 nm and 1053 nm[J]. Optics & Laser Technology, 2015, 68. |
| [11] Xu S , Wei Y , Huang C H , et al. Efficient end-pumped Q-switched 1053 nm Nd:YLF laser with a plane-parallel resonator[J]. Optics Communications, 2012, 285(6):1387-1389. |
| [12] Zhang H , D Li, Peng S , et al. Efficient, high power, Q-switched Nd:YLF slab laser end-pumped by diode stack[J]. Optics Communications, 2005, 250(1-3):157-162. |
| [13] Yan-Fei Lü, Zhang X H , Zhang A F , et al. Efficient 1047 nm CW laser emission of Nd:YLF under direct pumping into the emitting level[J]. Optics Communications, 2010, 283(9):1877–1879. |
| [14] Louyer Y , Balembois F , M.D. Plimmer, et al. Efficient cw operation of diode-pumped Nd:YLF lasers at 1312.0 and 1322.6 nm for a silver atom optical clock[J]. Optics Communications, 2003, 217(1-6):357-362. |
| [15] F Lindenberger, Stckl R , Laenen R , et al. Generation of intense 3 ps pulses by Kerr lens mode-locking of a pulsed Nd:YLF laser – ScienceDirect[J]. Optics Communications, 1995, 117(3):268-272. |
| [16] Armstrong M , Zhu X , Gracewski S , et al. Development of a 25 W TEMdiode-pumped Nd:YLF laser. 1999. |
| [17] Pan S , Lin X , Fan X , et al. Diode-pumped passively Q-switched mode-locked Nd:YLF laser with uncoated GaAs saturable absorber[J]. Optics Communications, 2007, 272(1):178-181. |
| [18] Veneri P D , Addonizio M L , Imparato A , et al. Application of Nd:YLF laser to amorphous silicon crystallization process[J]. Materials Science & Engineering B, 2000, 69(none):227-231. |
| [19] Xu, Shan, Gao, et al. A new wavelength laser at 1370 nm generated by Nd:YLF crystal[J]. Materials Letters, 2016. |
| [20] Li Y , Wang Q , Zhang S , et al. A novel La 3Ga 5SiO 14 electro-optic Q-switched Nd:LiYF (Nd:YLF) laser with a Cassegrain unstable cavity[J]. Optics Communications, 2005, 244(1-6):333-338. |
| [21] R. M , El-Agmy, N, et al. Power scaling of end-pumped Nd:YLF lasers, modeling and experiments[J]. Optik International Journal for Light & Electron Optics, 2017. |
| [22] Baldochi S L , Silva F R , Moraes J , et al. Synthesis and growth of materials for solid state lasers: Nd:YLF and Nd:LLW single crystal fibers[J]. Journal of Crystal Growth, 2011, 317(1):4-7. |
| [23] Jeong T M , Kang E C , Nam C H . Temporal and spectral characteristics of an additive-pulse mode-locked Nd:YLF laser with Michelson-type configuration[J]. Optics Communications, 1999, 166(1-6):95-102. |
| [24] [ D. Bergström, Powell J , Kaplan] A F H . The absorptance of steels to Nd:YLF and Nd:YAG laser light at room temperature[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2007. |
| [25] The formation and characterization of optical waveguide in Nd:YLF crystal by 4.5-MeV Si ion implantation[J]. Physica B Condensed Matter, 2018, 552. |
| [26] Zhong K , Yao J Q , Wang Y Y , et al. Comparison of eye-safe KTA OPOs pumped by Nd:YVO 4 and Nd:YLF lasers[J]. Optics & Laser Technology, 2011, 43(3):636-641. |
| [27] Wu R , Yang F , Lu J , et al. Research on beam quality improvement method of LD side-pumped acousto-optic Q-Switched anisotropic Nd:YLF laser[J]. Optik, 207. |
| [28] Bezotosnyi V V , Gorbunkov M V , Koromyslov A L , et al. Сoherent THz repetitive pulse generation in a GaSe crystal. 2015. |
| [29] Dai Q , Zhang S , Li Y , et al. Study of high beam quality side-pumped Nd:YLF laser with intracavity Gaussian aperture[J]. Optik, 2019, 176:655-661. |
| [30] Heinz P , Seilmeier A , Piskarskas A . Picosecond Nd:YLF laser-multipass amplifier source pumped by pulsed diodes for the operation of powrful OPOs[J]. Optics Communications, 1997, 136(5):433-436. |



Leave a Reply