Er:YLF
Er3+:YLF crystals are characterized by low phonon frequency, which decreases the probability of non-radiative multi-phonon relaxations, therefore increases luminescence quantum efficiency. Long lifetime of laser emitting levels allow higher energy storage, which is useful for the Q-switch lasing regime. High band-gap along with low phonon energy determines very wide transparency range, which is possibly from VUV to 10μm region. Negative Er3+:YLF thermo-optic coefficient is an advantage, since it reduces thermal-lensing effect and improves beam shape as well as stability at high average pump power.
Parameter
| Orientation | A-cut |
| Parallelism | <10〞 |
| Perpendicularity | <10ˊ |
| Surface Quality | 10-5 S-D |
| Wavefront Distortion | <λ/4 per inch@632.8 nm |
| Surface Flatness | <λ/10 @632.8 nm |
| Clear Aperture | >90% |
| Face Dimensions Tolerance | +0.0/-0.1 mm |
| Length Tolerance | ±0.1mm |
| Chamfer | <0.1mm@45° |
| Structure Symmetry | Tetragonal |
| Lattice Constants | a=5.173, c=10.747 Å@1.5% |
| Specific mass | 3.95g/cm3 |
| Melting Point | 819°C |
| Thermal Conductivity /(W·m-1·K-1) | ~5 |
| Specific Heat(J·g-1·K-1) | 0.79 |
| Thermal Expansion /(10-6·K-1 ) | 8 |
| Hardness (kg/mm2@Mohs) | 5 |
| Young`s Modulus /(108g/cm2) | 7.65 |
| Typical Doping Level | 15@.% |
| Refractive Index (@2070nm) | no=1.442, ne=1.464 |
| Thermo-optic Coefficient(10-6·K-1) | -2(∥a), -4.1(∥c) |
| Lifetime of 4I11/2 Erbium Energy Level(ms) | 4 |
| Emission Cross Section(10-20/cm2) | 1.5@2800nm |
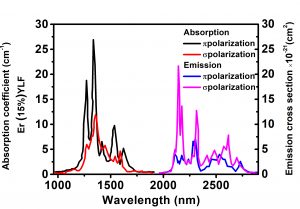
| Absorption Peak Wavelength | 972nm |
| Absorption Coefficient at Peak Wavelength | 28cm-1 |
| Absorption Bandwidth at Peak Wavelength | ~1nm |
| Laser Wavelength | 2810nm |
Feature
Application
Literature
Feature
- A low phonon frequency
- Long lifetimes of the laser emitting levels
- Wide transparency range (from the VUV to the 10 μm region)
- Negative thermo-optic coefficient
- Custom crystals available upon request
Application
- CW and Q-switched ~3 μm lasers for oral surgery, dentistry, implant dentistry, and otolaryngology
- Up-conversion visible lasers for display technology, medicine (diagnosis and treatment)
Literature
| [1] Tikerpae, M, Jackson, et al. 2.8 @mm Er:YLF laser transversely pumped with a CW diode laser bar[J]. OPTICS COMMUNICATIONS, 1999. |
| [2] Mateos X , Pujol M C , F Güell, et al. Infrared-to-green up-conversion in Er 3+, Yb 3+-doped monoclinic KGd(WO 4) 2 single crystals[J]. Optical Materials, 2004, 27(3):475-479. |
| [3] Petrov V . Frequency down-conversion of solid-state laser sources to the mid-infrared spectral range using non-oxide nonlinear crystals[J]. Progress in Quantum Electronics, 2015, 42:1-106. |
| [4] Ulc J , H Jelínková. Solid-state lasers for medical applications[J]. Lasers for Medical Applications, 2013:127-176. |
| [5] Tang, C. L , Bosenberg, et al. Optical parametric oscillators[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 1992, 80(3):365-374. |
| [6] Toma O , Georgescu S . Competition between green and infrared emission in Er:YLiF 4 upconversion lasers[J]. Optics Communications, 2011, 284(1):388-397. |
| [7] W Lüthy, Weber H P . Diode-pumped IR solid-state lasers[J]. Infrared Physics & Technology, 1995, 36(1):267-272. |
| [8] Moloney J V , AC Newell. Nonlinear optics[J]. Physica D Nonlinear Phenomena, 1990, 44(1):1-37. |
| [9] Fornasiero L , Mix E , Peters V , et al. Czochralski growth and laser parameters of RE3+-doped Y2O3 and Sc2O3[J]. Ceramics International, 2000, 26(6):589-592. |
| [10] Jiaqi, Hong, Lianhan, et al. Effect of erbium concentration on optical properties of Er:YLF laser crystals[J]. Infrared Physics & Technology, 2017. |
| [11] Liithy W , Weber P , Rogin P , et al. Emission properties of an optimised 2.8 brn Er”+:YLF laser. 1997. |
| [12] Huailiang, Xu, and, et al. Dynamics of visible-to-ultraviolet upconversion in YAlO3: 1% Er3+[J]. Chemical Physics, 2003, 287(1-2):155-159. |
| [13] None. Author index to Volumes 161–170[J]. Applied Mathematics & Computation, 2005, 170(2):1477–1531. |
| [14] Favilla E , Cittadino G , Veronesi S , et al. Comparative analysis of upconversion efficiencies in fluoride materials for photovoltaic application[J]. Solar Energy Materials and Solar Cells, 2016, 157:415-421. |
| [15] Godard A . Infrared (2–12 μm) Solid-State Laser Sources: A Review[J]. Comptes Rendus Physique, 2007, 8(10):1100-1128. |
| [16] A P, Loiko, A E,等. Judd–Ofelt analysis and stimulated-emission cross-sections for highly doped (38 at%) Er:YSGG laser crystal[J]. Journal of Luminescence, 2016. |
| [17] Hazenkamp M F , HU Güdel. Luminescence properties of solids[J]. Current Opinion in Solid State & Materials Science, 1996, 1(2):177-182. |
| [18] Bonelli L , Cornacchia F , Tonelli M , et al. Spectroscopic properties of Er:NaLa(WO4)2 crystals and effect of Ce codoping onto the excited state energy transformation in this crystal[J]. Journal of Luminescence, 2013, 135:178-186. |
| [19] Fornasiero L , Petermann K , Heumann E , et al. Spectroscopic properties and laser emission of Er 3+ in scandium silicates near 1.5 μm[J]. Optical Materials, 1998, 10(1):9-17. |
| [20] Thorleuchter D , Poel D . Technology classification with latent semantic indexing[J]. Expert Systems with Applications: An International Journal, 2013. |
| [21] You W , Huang Y , Chen Y , et al. The Yb3+ to Er3+ energy transfer in YAl3(BO3)4 crystal[J]. Optics Communications, 2008, 281(19):4936-4939. |
| [22] Scheps R . Upconversion laser processes[J]. Progress in Quantum Electronics, 1996, 20(4):271-358. |
| [23] Camargo M B , Gomes L , Morato S P . Quantitative analysis of erbium luminescente in LiYF, doped with low ( 1.41%) and high (38.5%) Ert3 concentrations. |
| [24] Huber G , Heumann E , Sandrock T , et al. Up-conversion processes in laser crystals[J]. Journal of Luminescence, 1997, 72(96):1-3. |
| [25] Bibliography Current World Literature[J]. Current Opinion in Pediatrics, 2000, 12. |
| [26] Walsh B M , Lee H R , Barnes N P . Mid infrared lasers for remote sensing applications[J]. Journal of Luminescence, 2016, 169. |
| [27] Upconversion in Er3+:YA103 produced by metastable state absorption |
| [28] Diode-pumped high power 2.7 m m Er:Y 2 O 3 ceramic laser at rooM temperature |
| [29] Concentration effects on the IR-luminescent channels for Er- and Ho-doped LiYF 4 crystals |
| [30] LASERS |


Leave a Reply